Toon has a Master’s Degree in Civil Engineering (major in Energy) from the KU Leuven. He completed a 6 month internship as Derivates Analist. He work as a Junior Climate Consultant for Econopolis Climate and works on advisory projects related to climate & energy. Toon is also founder of Stroomloop, a unique trailrunning experience.
Rising Tide of Solar Power: Exploring the Growth of PV and Floating PV Installations

The global transition to clean and renewable energy sources has significantly accelerated in recent years, with solar photovoltaic (PV) installations spearheading this movement. The statistics are nothing short of impressive: a staggering 1,047 gigawatts (GW) of solar PV systems have been installed worldwide, representing a remarkable twenty-six-fold growth since 2010. In 2022 alone, 191 GW of new PV systems were commissioned globally, with China taking the lead, accounting for 77% of all Asian additions and 45% of all global additions. This surge in solar PV adoption can be attributed to a significant decline in module costs, which has made solar energy competitive with conventional fossil-fuel-fired-powered electricity generation plants.
The exponential growth rates and consecutive year-on-year records in solar photovoltaic (PV) installations have catalyzed the proliferation of companies producing essential PV components. Although the industry has been predominantly dominated by Chinese manufacturers, companies in the European Union (EU) have also established a significant foothold in this dynamic sector. These EU firms not only contribute to the global shift towards renewable energy, but also foster economic growth within their own regions.
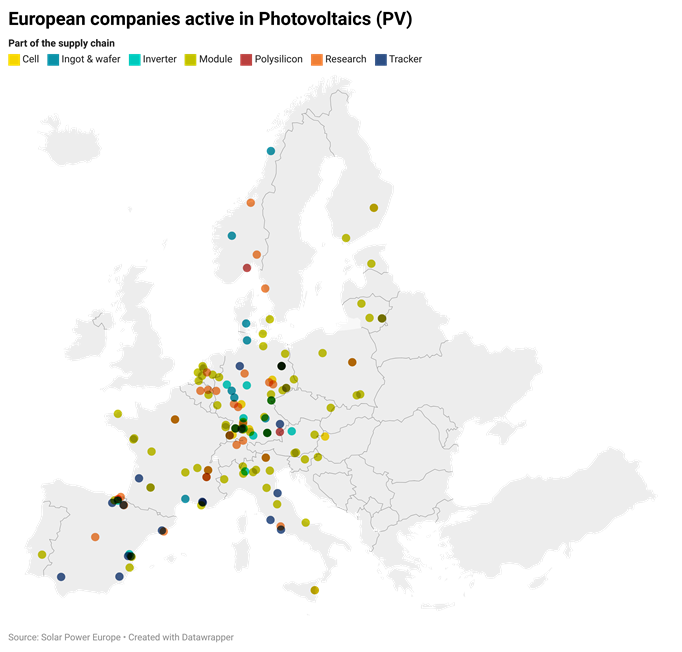
Figure 1. Source: Solar Power Europe
As the demand for solar power continues to soar, several countries are grappling with space limitations for traditional ground-mounted installations. To circumvent this challenge, they are exploring the prospects of “floating PV installations”, wherein photovoltaic panels are strategically positioned over inland and nearshore water bodies. While this innovative approach presents numerous advantages, it also brings forth a set of challenges that need to be addressed. To make this concept work, countries need large floating structures and water-tight cables to transfer the generated energy to the mainland. Despite the complexities involved, the installed capacity of floating PV systems has been steadily increasing year after year. According to Wood MacKenzie, a global energy research and consultancy group, there is an anticipated average annual growth rate of 12% over the next decade, highlighting the potential of this emerging technology.
While floating PV holds great promise, it's important to acknowledge the drawbacks associated with this approach. One of the primary challenges is the increased cost compared to traditional solar installations. The need for robust floating structures, higher standards for cabling, and additional maintenance to clean the panels all contribute to a higher levelized cost of electricity (LCOE), a financial measure that represents the per-unit cost (typically per megawatt-hour) of building and operating a generating plant over an assumed financial life and duty cycle. The precise LCOE can vary depending on factors such as location and technology used, but it tends to be between 10 and 20% higher than land-based PV systems.
Furthermore, the potential impact on underwater ecosystems is a concern that must be thoroughly studied and addressed. The deployment of floating PV arrays could disturb aquatic habitats, making it vital to lessen these effects through careful planning and stringent environmental monitoring.
Despite the challenges, floating PV installations offer several significant advantages:
- Efficient Space Utilization: Countries with limited land availability, like Belgium, can optimize their solar power generation by utilizing water bodies for PV installations. By fully utilizing Belgium’s inland water bodies with this technology, floating PV systems could potentially be strategically interspersed between offshore wind turbines in the North Sea, amplifying the overall power output per unit of surface area.
- Improved Efficiency: Floating PV systems benefit from passive cooling due to their proximity to water, which can yield a slightly higher energy conversion efficiency compared to traditional PV installations.
- Reduced Water Evaporation: Installing PV panels on water bodies can help reduce the evaporation rate of these water bodies, making it particularly beneficial for reservoirs used for hydropower generation.
- Emerging Market Opportunities: The increasing adoption of floating PV installations worldwide has spurred the active participation of European companies in international tenders. Europe is strategically positioning itself to become a prominent player in this emerging market, with numerous companies seeking to establish a strong presence and contribute to the growth of renewable energy.
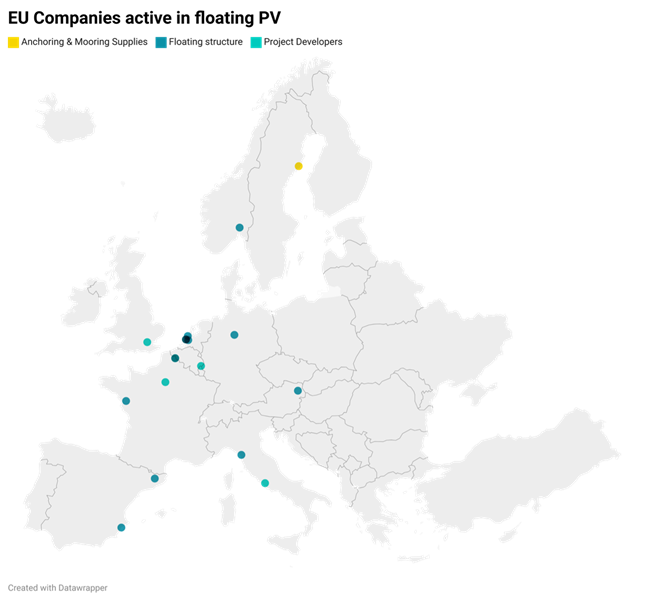
The global growth of solar PV installations, along with the emerging trend of floating PV systems, heralds a promising future for renewable energy. As the global community steadfast shifts away from fossil fuels, innovative solutions like floating PV become essential in surmounting space limitations and fully tapping into the sun’s potential as an energy source. While certain challenges exist, the benefits of floating PV installations are unequivocal, offering more efficient land use and environmentally friendly advantages. As European companies actively participate in this market, the outlook for the renewable energy sector is brighter than ever.
